
https://talk.newagtalk.com/forums/thread-view.asp?tid=818667&mid=7122411#M7122411 and over a b bushels.....if we happen to get a china deal this could be huge
gleaner
yes those with gleanors are not done yet,,,,,,ha

22,222
GO TIME
Are you talking about the Silver Seeders?
yes silver spikers and silver seeders
I recognize that equation SS!
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rayleigh_scattering
Figure showing the greater proportion of blue light scattered by the atmosphere relative to red light.
This is what causes the sky to "appear" to our eyes to be blue because we only see what the dominant color is in the visible spectrum(the one that's bouncing around up there the most after being refracted out by the tiny nitrogen molecules).
What does this have to do with soybeans?
Nothing really...........but how about this.
Soybeans use several sources to produce thru photosynthesis, including energy from the sun.
Sun +H20 + CO2 + Minerals = Sugars(food) + O2.
What part of the solar energy spectrum do plants, crops, beans use?????
Much of it is in the visible spectrum.
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/ligabs.html
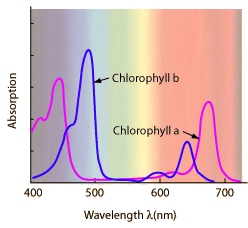 | Photosynthesis depends upon the absorption of light by pigments in the leaves of plants. The most important of these is chlorophyll-a, but there are several accessory pigments that also contribute. |
| The measured rate of photosynthesis as a function of absorbed wavelength correlates well with the absorption frequencies of chlorophyll a, but makes it evident that there are some other contributors to the absorption. | 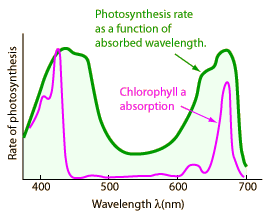 |


So why are leaves green?
Notice the huge dip in the center of the graphs above. This corresponds to the green part of the visible spectrum. Plants ARE NOT absorbing the light in the green part of the spectrum to make food, so we see what they "leave" behind.
We say that chlorophyll is green(it is) because the chlorophyll REFLECTS the green part of the visible spectrum and absobs much of the rest of the visible light to use in photosynthesis.
Light is a form of energy. The form of light that plants capture, as well as the light that you and I can see, is called visible light. The white light that shines on Earth from the sun is actually composed of light of many different colors.
The science of using growing lights inside to grow plants:
Wavelengths are what we use to measure a wave along the electromagnetic spectrum, and they can be longer waves like radio waves or shorter like gamma rays. But no matter if it’s x-ray’s for your bones or TV waves you get from satellites, wavelengths are what you need to manipulate in order to get the results you want.
Thankfully the spectrum we’re referring to is the light spectrum, which- in the grand scheme of things- is relatively small. Even better, when it comes to growing plants there are really only four wavelengths of light we consider: blue (cool, 400-520nm), green (neutral, 500-600nm), red (warm, 630-660nm), and beyond red (hot, 720-740nm). These wavelengths are vital when it comes to growing plants because they will allow a plant to process light and sugars properly, as well as encourage your plants to grow and protect itself in various ways.
Good God Man.....
Photosynthesisis ???.... so 1911....ppfffftttt....