
Space Ambient Music • Deep Space Relaxation Scenes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mfoRx20c7Us
https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/are-we-really-made-of-stardust.html
'It is totally 100% true: nearly all the elements in the human body were made in a star and many have come through several supernovas.'

Carbon =18.5%!
Where do you think that carbon comes from?
https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/earth-system/biogeochemical-cycles
There are a few types of atoms that can be a part of a plant one day, an animal the next day, and then travel downstream as a part of a river’s water the following day. These atoms can be a part of both living things like plants and animals, as well as non-living things like water, air, and even rocks. The same atoms are recycled over and over in different parts of the Earth. This type of cycle of atoms between living and non-living things is known as a biogeochemical cycle.
All of the atoms that are building blocks of living things are a part of biogeochemical cycles. The most common of these are the carbon and nitrogen cycles.
Tiny atoms of carbon and nitrogen are able to move around the planet through these cycles. For example, an atom of carbon is absorbed from the air into the ocean water where it is used by little floating plankton doing photosynthesis to get the nutrition they need. There is the possibility that this little carbon atom becomes part of the plankton’s skeleton, or a part of the skeleton of the larger animal that eats it, and then part of a sedimentary rock when the living things die and only bones are left behind. Carbon that is a part of rocks and fossil fuels like oil, coal, and natural gas may be held away from the rest of the carbon cycle for a long time. These long-term storage places are called “sinks”. When fossil fuels are burned, carbon that had been underground is sent into the air as carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas.
Recently, people have been causing these biogeochemical cycles to change. When we cut down forests, make more factories, and drive more cars that burn fossil fuels, the way that carbon and nitrogen move around the Earth changes. These changes add more greenhouse gases in our atmosphere and this causes (MOSTLY BENEFICIAL-MM) climate change.

The element carbon is a part of seawater, the atmosphere, rocks such as limestone and coal, soils, as well as all living things. On our dynamic planet, carbon is able to move from one of these realms to another as a part of the carbon cycle.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and traps heat in the atmosphere. Without it and other greenhouse gases, Earth would be a frozen world.
https://ugc.berkeley.edu/background-content/carbon-cycle/

While most of the Earth’s carbon can be found in the geosphere, carbon is found in all living things, soils, the ocean, and atmosphere. Carbon is the primary building block of life, including DNA, proteins, sugars and fats. One of the most important carbon compounds in the atmosphere is carbon dioxide (CO2),
Death by GREENING!
https://www.marketforum.com/forum/topic/69258/
 ++++++++++++++++
++++++++++++++++
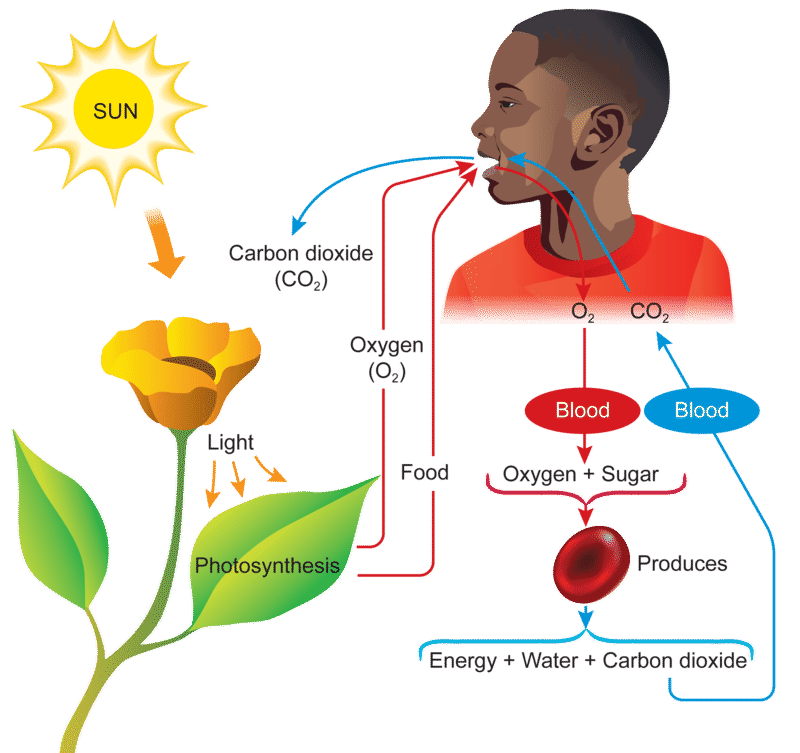
https://www.ck12.org/book/human-biology-breathing/section/4.1/

https://www.co2meter.com/blogs/news/carbon-dioxide-indoor-levels-chart
Normal CO2 levels in fresh air is approximately 400 ppm (part per million) or 0.04% CO2 in air by volume. The table below shows the effects of increased CO2 levels in an enclosed space as a percent of air by volume.
This site is selling CO2 meters. I made some corrections and adjustments to their information below based on authentic science. Those are underlined and in CAPS.
| 420ppm 0.04% | Normal outdoor air-HEALTHY |
| 400-1,000ppm 0.04-0.1% | Typical CO2 levels found indoors-HEALTHY |
| 1,000-2,000ppm 0.1-0.2% | "POSSIBLE" complaints of drowsiness or poor air quality-STILL SAFE |
| 2,000-5,000ppm 0.2-0.5% | "POSSIBLE" Headaches, fatigue, stagnant, stuffiness, poor concentration, loss of focus, increased heart rate, nausea-UNHEALTY BUT NOT FATAL |
| > 50,000ppm > 5% | Toxicity due to oxygen deprivation occurs |
| > 100,000ppm > 10% | Oxygen deprivation in seconds: convulsions, coma, and death |
metmike: The increase in beneficial CO2, instead of killing the planet has rescued the planet from near CO2 starvation 150 years ago!
290 ppm(parts per million) was dangerously low for life.
Currently, 420 ppm is still LESS THAN half the OPTIMAL level for most life on the planet.
https://extension.okstate.edu/fact-sheets/greenhouse-carbon-dioxide-supplementation.html
Generally, doubling ambient CO2 level (i.e. 700 to 800 parts per million) can make a significant and visible difference in plant yield. Plants with a C3 photosynthetic pathway (geranium, petunia, pansy, aster lily and most dicot species) have a 3-carbon compound as the first product in their photosynthetic pathway, thus are called C3 plants and are more responsive to higher CO2 concentration than plants having a C4 pathway (most of the grass species have a 4-carbon compound as the first product in their photosynthetic pathway, thus are called C4 plants). An increase in ambient CO2 to 800-1000 ppm can increase yield of C3 plants up to 40 to 100 percent and C4 plants by 10 to 25 percent while keeping other inputs at an optimum level. Plants show a positive response up to 700 to need of 1,800 parts per million, but higher levels of CO2 may cause plant damage
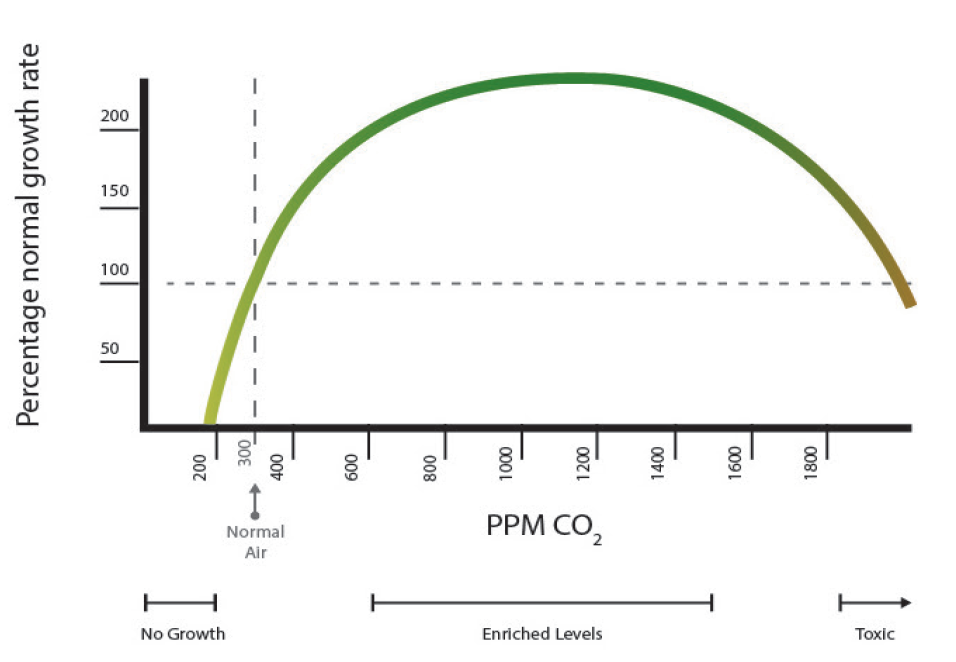 Figure 1. Relation between CO2 concentration and rate of plant growth. Source: Roger H. Thayer, Eco Enterprises, hydrofarm.com. Redrawn by Vince Giannotti.
Figure 1. Relation between CO2 concentration and rate of plant growth. Source: Roger H. Thayer, Eco Enterprises, hydrofarm.com. Redrawn by Vince Giannotti.

More CO2 = More Food for all life
That is indisputable!